Project
Embodied AI for biotech experiments robot
Internship project in Centrillion Technology

keywords: Embodied AI, Imitation Learning, LLM, Biotech Experimental Robot
• Use Mobile-ALOHA platform to to collect expert trajectories (more than 500 episodes per subtask) to build a dataset with 15+ subtasks.
• Use ACT algorithm to train 15+ biological experiment fine operation subtasks. Single subtask duration 10-20s, success rate of more than 80%, with basic generalization and adaptive ability.
• Design an embodied AI framework using LLM and imitation learning, conducting high-level task planning, estimating the success of the previous subtask, and executing the sequenced subtask under the premise of safety to ensure seamless integration of robot functions in the complex experimental workflow.
Example video of LLM driven embodied AI (manuplation + base moving) can be found here
Example video of generalized pick-and-place task can be found here
Example video of using syringe to conduct biochemical experimet task can be found here
Example video of accurate manipulation in moving wafer can be found here
Example video of generalized manipulation in moving wafer can be found here
Deep reinforcement learning based quadrupedal robot control and locomotion development
Internship project in Unitree Robotics
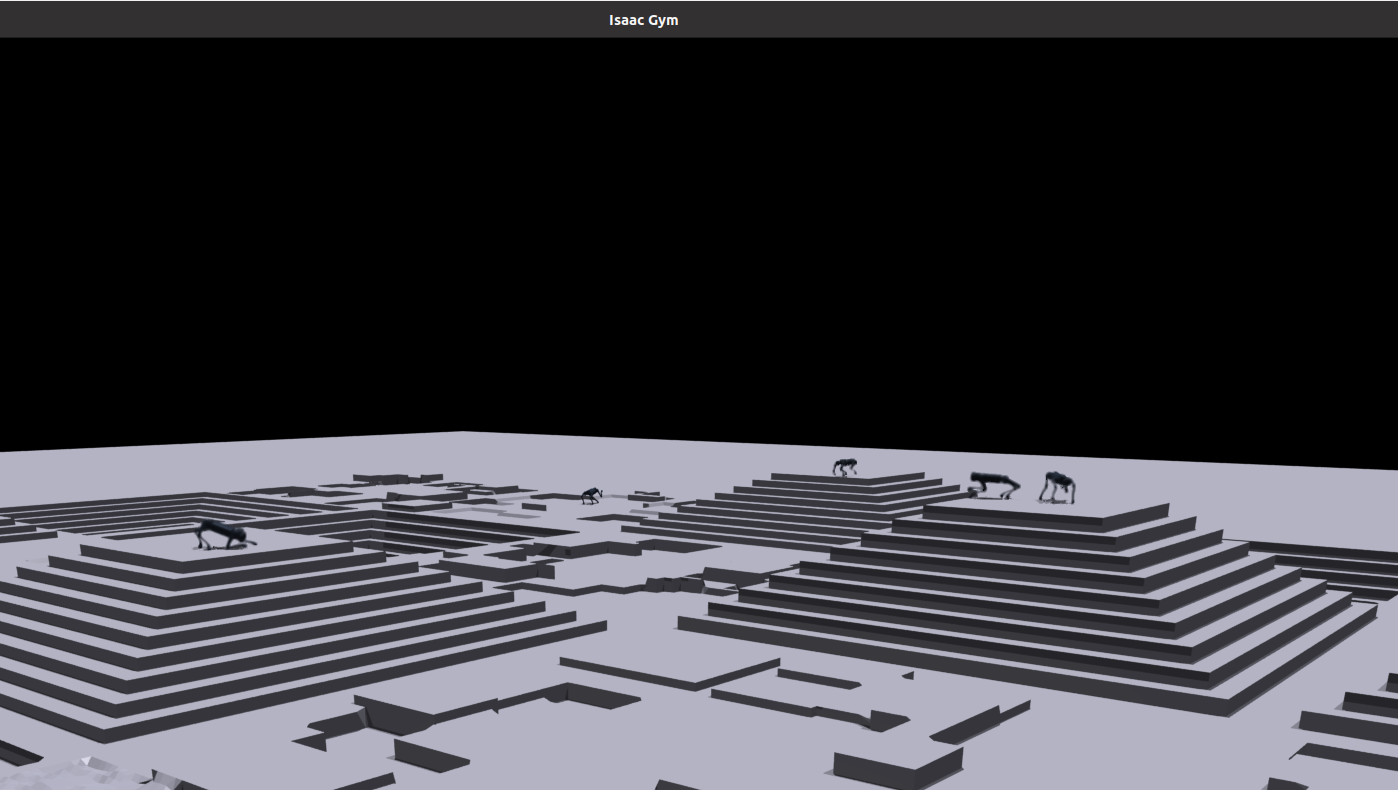
Deep reinforcement learning involves training a robot to navigate and control its movements by learning from its interactions with the environment. The project focuses on the development of robot locomotion and controls through the implementation of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) techniques. The project aims to enhance the robustness, efficiency, and adaptability of robotic systems, paving the way for more sophisticated and autonomous robots capable of navigating complex environments with precision and intelligence.
What I have done in this project:
• Developed the novel quadrupedal robot locomotion and controls framework with deep reinforcement learning that increases the robot payload by 15% compared with traditional model-based control framework
• Trained the quadrupedal robot locomotion and controls policy based on deep reinforcement learning with Isaac Gym
• Developed the quadrupedal robot learning-based locomotion and controls model deployment program with C++
• Conduct quadrupedal robot multi-gaits walking test using trained deep reinforcement learning control policy and analyzed the test data for sim-to-real evaluation
• Developed the quadrupedal robot state estimator using sensor fusion techniques based on Extended Kalman Filter, increasing the estimation accuracy by 23%
Example video can be found here
Intelligent Sign Language Robot Development
Team Leader, Capstone Project of ZJU-UIUC Institute
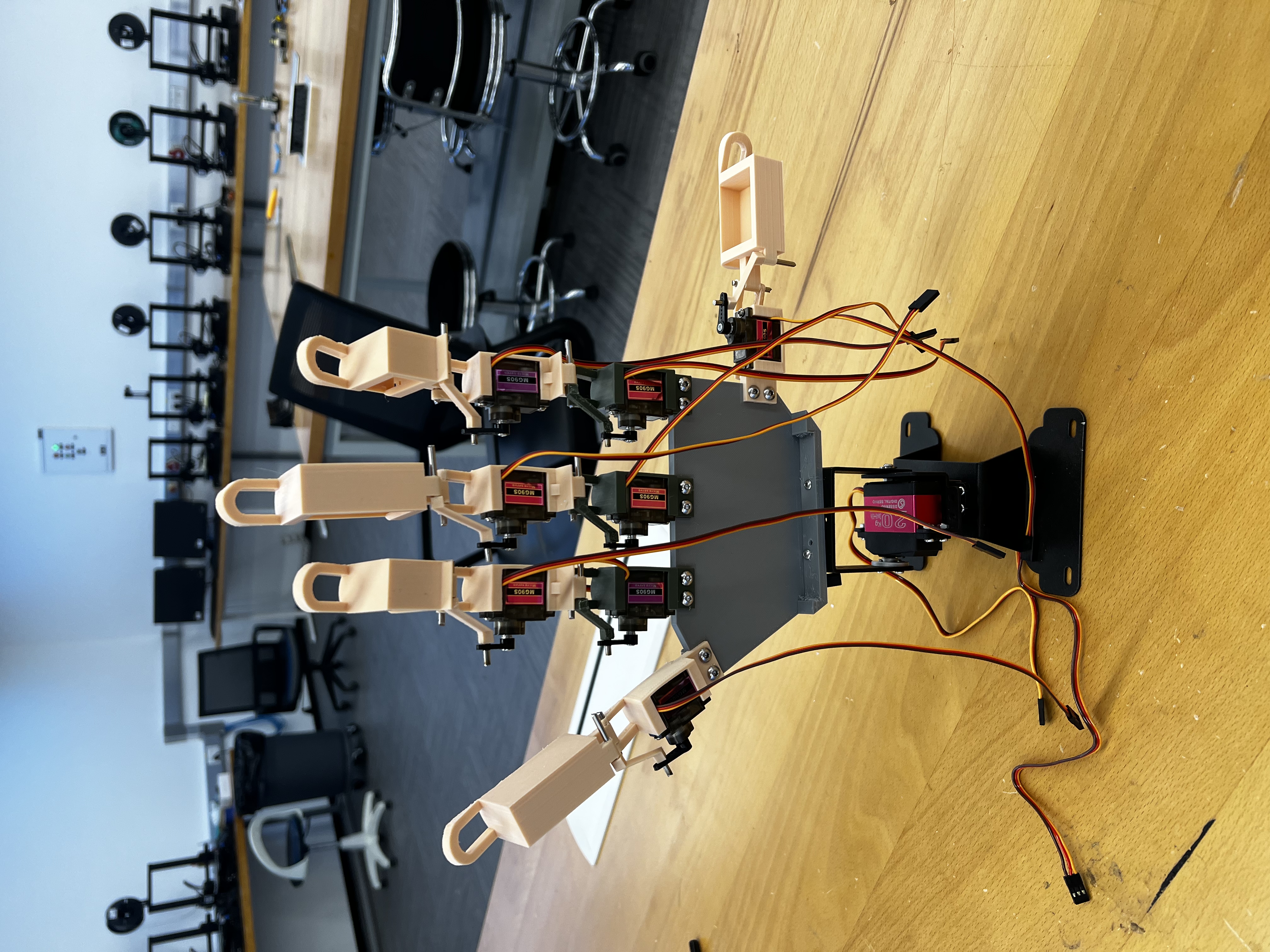
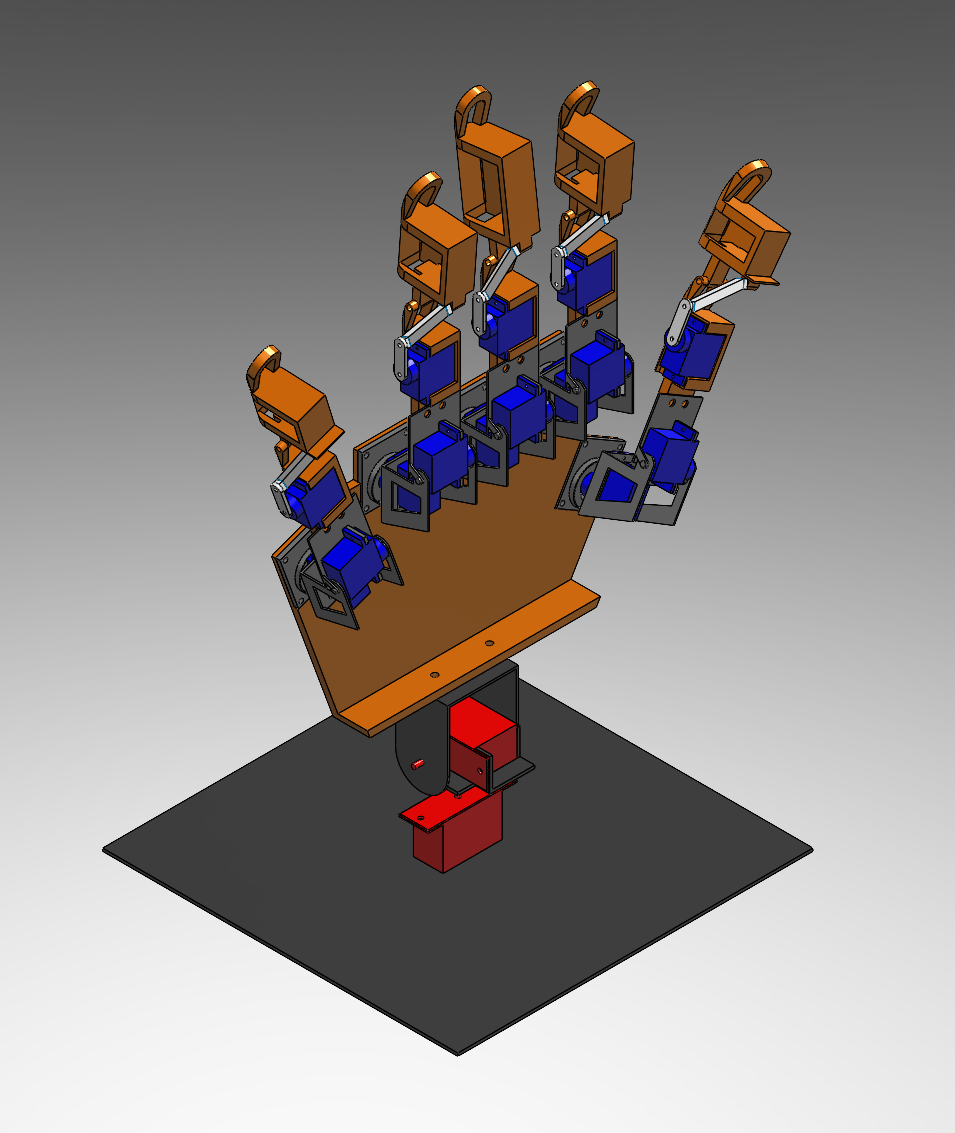
This project proposes a novel intelligent assistant to help people with speech or hearing impairments communicate and seek help. The intelligent assistant includes a bionic hand of 17 degrees of freedom (DOFs) and an innovative neural network that recognizes American Sign Language (ASL). The users can prompt a question in ASL, and the assistant would recognize the problem and search for the answer online, answering and helping the user with ASL co-generated by the microcontroller unit and the bionic hand. Meanwhile, the answer would be demonstrated on a digital screen for inspection.
What I have done in this project:
• Designed and developed the sign language robot hardware system, including a 17 degrees of freedom dexterous bionic hand, a STM-32 microcontroller, a NVIDIA Jetson Nano onboard computer
• Developed the control algorithm and program of the robot, designed the movement of each joint motor based on standard American Sign Language
• Co-developed the image detection program to identify customer’s sign based on YOLO-V5
Project final paper can be found here, demonstration video can be found here
